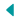
The Eastern Red Columbine (Aquilegia canadensis) is a native perennial wildflower that brings vibrant beauty and ecological benefits to  gardens across the Eastern United States. Known for its striking red and yellow nodding flowers, this plant is a favorite among gardeners and pollinators alike.
gardens across the Eastern United States. Known for its striking red and yellow nodding flowers, this plant is a favorite among gardeners and pollinators alike.
Key Characteristics
Zones: 3–8
Height: 2–3 feet
Bloom Time: March–May
-
Features: Graceful, bell-shaped flowers with red spurs and yellow tips, complemented by delicate, fern-like foliage.
The flowers’ unique shape gives the plant its scientific name, derived from aquila, Latin for “eagle,” as the spurs resemble an eagle’s talons. These blooms are not only visually stunning but also serve as a vital nectar source for hummingbirds, butterflies, and bees during early spring.
Eastern columbine, Aquilegia canadensis is a perennial native wildflower that is easy to grow, attracts a wide range of pollinators, and is especially liked by hummingbirds. In addition, it is the sole host plant for the columbine duskywing butterfly, a type of skipper. If you love hummingbirds and bright showy wildflowers the eastern columbine is a must have for your garden! Watch the video and learn all about Eastern Columbine!
Natural Habitat
Eastern Red Columbine thrives in diverse environments, including rocky slopes, woodland edges, and cliffs. Its adaptability to various soil types— provided they are well-drained—makes it a versatile choice for naturalized areas or shade gardens. The plant’s ability to self-seed allows it to form colonies over time, creating a lush display in suitable conditions.
provided they are well-drained—makes it a versatile choice for naturalized areas or shade gardens. The plant’s ability to self-seed allows it to form colonies over time, creating a lush display in suitable conditions.
Care and Maintenance
This low-maintenance wildflower is both deer- and drought-resistant, making it an excellent option for gardeners seeking resilient plants. While it prefers light shade or dappled sunlight, it can tolerate full sun if the soil remains moist. To ensure healthy growth:
Avoid overwatering during hot summers to prevent crown rot.
Cut back spent flowers to encourage fresh foliage and potential reblooming.
Remove other Aquilegia species nearby to prevent hybridization and preserve its native genetics.
Ecological Benefits
Eastern Red Columbine is a powerhouse for pollinator support. Its tubular flowers are perfectly suited for hummingbirds, which act as primary pollinators. Additionally, butterflies and native bees benefit from its nectar. The plant’s foliage also serves as a host for certain caterpillar species.
Garden Uses
This adaptable plant fits seamlessly into various garden styles
Woodland Gardens: Add color to shaded areas with its vibrant blooms.
Pollinator Gardens: Support hummingbirds and other pollinators during their active seasons.
Rock Gardens: Its natural affinity for rocky terrains makes it ideal for such settings.
Cut Flower Arrangements: The long-lasting blooms add elegance to floral displays.
Why Choose Eastern Red Columbine?
With its stunning appearance, ecological value, and adaptability, Eastern Red Columbine is a must-have for gardeners looking to enhance their landscapes while supporting native wildlife. Whether planted in borders, naturalized areas, or under trees, this wildflower is sure to captivate with its charm and resilience.
What are the unique characteristics of Eastern Red Columbine that make it attractive to hummingbirds
Eastern Red Columbine (Aquilegia canadensis) is a native wildflower with several unique traits that make it highly appealing to hummingbirds. Its vibrant blooms, specialized floral structure, and ecological timing ensure it remains a favorite among these pollinators.
- Bright Red and Yellow Flowers
The striking red and yellow coloration of Eastern Red Columbine’s flowers is one of its most defining features. Hummingbirds are naturally drawn to bright colors, particularly red, which signals a rich nectar source. The nodding flowers stand out in woodland or garden settings, making them easy for hummingbirds to locate.
- Talon-Shaped Spurs
The flowers of Eastern Red Columbine feature elongated, tubular spurs filled with sweet nectar. These spurs are perfectly adapted to the long bills and tongues of hummingbirds, allowing them to access nectar deep within the flower. As hummingbirds feed, they inadvertently collect pollen on their heads and transfer it between flowers, ensuring successful pollination.
- High Nectar Content
Eastern Red Columbine produces nectar with a high sugar concentration, providing hummingbirds with the energy they need for their rapid flight and high metabolism. The nectar’s sugar content is notably higher than many other wildflowers, making it an essential food source during the birds’ migration period.
- Seasonal Synchronization
The blooming period of Eastern Red Columbine (March–May) coincides with the return of migrating Ruby-throated Hummingbirds in early spring. This co-evolution ensures that hummingbirds have access to abundant nectar just when they need it most after their long journey north.
- Adaptability
Eastern Red Columbine thrives in various conditions, from rocky woodlands to shaded gardens. Its ability to self-seed allows it to form large colonies over time, creating dense feeding grounds for hummingbirds.
With its vibrant flowers, specialized spurs, and high nectar production, Eastern Red Columbine is a vital plant for attracting hummingbirds while supporting pollinator health in native ecosystems.
Natural Pest Control Methods for Your Hummingbird Garden
Creating a thriving hummingbird garden is a rewarding experience. However, maintaining it while keeping pests at bay can be challenging. Fortunately, there are numerous natural pest control methods that can protect your garden’s delicate ecosystem. Click the link above to find out how to naturally control pests in your hummingbird garden.
Here are 3 authoritative links where you can find more information about hummingbirds:
National Park Service: https://www.nps.gov/articles/hummingbirds.htm
Oregon State University Extension Service: https://extension.oregonstate.edu/outdoors-environments/wildlife/9-fast-facts-hummingbirds
University of Florida IFAS Extension: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/UW059
These sites offer reliable, science-based information on hummingbird biology, behavior, and conservation from reputable educational and governmental institutions.