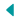
Hummingbirds are enchanting garden visitors, known for their vibrant plumage and rapid wingbeats. To attract these remarkable birds, planting native flora is essential. Native plants not only provide high-quality nectar but also support local ecosystems by attracting insects and other pollinators. This comprehensive guide explores a variety of native plants ideal for hummingbird gardens in the Eastern United States, ensuring blooms throughout the growing season.
Why Choose Native Plants?
Native plants are naturally adapted to local conditions, making them easier to grow and maintain. They offer several benefits:
-
High nectar content: Native flowers provide abundant nectar, which hummingbirds rely on for energy.
-
Support for insects: Hummingbirds supplement their diet with protein-rich insects attracted by native plants.
-
Environmental resilience: Native species thrive in local climates and soils, reducing the need for fertilizers and excessive watering.
Top Native Plants by Season
Spring Bloomers
Spring blooms are crucial for hummingbirds returning from migration, providing much-needed nectar after their long journey.
1. Eastern Red Columbine (Aquilegia canadensis): A Native Gem for Your Garden
The Eastern Red Columbine (Aquilegia canadensis) is a native perennial wildflower that brings vibrant beauty and ecological benefits to  gardens across the Eastern United States. Known for its striking red and yellow nodding flowers, this plant is a favorite among gardeners and pollinators alike.
gardens across the Eastern United States. Known for its striking red and yellow nodding flowers, this plant is a favorite among gardeners and pollinators alike.
Key Characteristics
-
Zones: 3–8
-
Height: 2–3 feet
-
Bloom Time: March–May
-
Features: Graceful, bell-shaped flowers with red spurs and yellow tips, complemented by delicate, fern-like foliage.
The flowers’ unique shape gives the plant its scientific name, derived from aquila, Latin for “eagle,” as the spurs resemble an eagle’s talons. These blooms are not only visually stunning but also serve as a vital nectar source for hummingbirds, butterflies, and bees during early spring.
Natural Habitat
Eastern Red Columbine thrives in diverse environments, including rocky slopes, woodland edges, and cliffs. Its adaptability to various soil types— provided they are well-drained—makes it a versatile choice for naturalized areas or shade gardens. The plant’s ability to self-seed allows it to form colonies over time, creating a lush display in suitable conditions.
provided they are well-drained—makes it a versatile choice for naturalized areas or shade gardens. The plant’s ability to self-seed allows it to form colonies over time, creating a lush display in suitable conditions.
Care and Maintenance
This low-maintenance wildflower is both deer- and drought-resistant, making it an excellent option for gardeners seeking resilient plants. While it prefers light shade or dappled sunlight, it can tolerate full sun if the soil remains moist. To ensure healthy growth:
-
Avoid overwatering during hot summers to prevent crown rot.
-
Cut back spent flowers to encourage fresh foliage and potential reblooming.
-
Remove other Aquilegia species nearby to prevent hybridization and preserve its native genetics.
Ecological Benefits
Eastern Red Columbine is a powerhouse for pollinator support. Its tubular flowers are perfectly suited for hummingbirds, which act as primary pollinators. Additionally, butterflies and native bees benefit from its nectar. The plant’s foliage also serves as a host for certain caterpillar species.
Garden Uses
This adaptable plant fits seamlessly into various garden styles:
-
Woodland Gardens: Add color to shaded areas with its vibrant blooms.
-
Pollinator Gardens: Support hummingbirds and other pollinators during their active seasons.
-
Rock Gardens: Its natural affinity for rocky terrains makes it ideal for such settings.
-
Cut Flower Arrangements: The long-lasting blooms add elegance to floral displays.
Why Choose Eastern Red Columbine?
With its stunning appearance, ecological value, and adaptability, Eastern Red Columbine is a must-have for gardeners looking to enhance their landscapes while supporting native wildlife. Whether planted in borders, naturalized areas, or under trees, this wildflower is sure to captivate with its charm and resilience.
What are the unique characteristics of Eastern Red Columbine that make it attractive to hummingbirds
Eastern Red Columbine (Aquilegia canadensis) is a native wildflower with several unique traits that make it highly appealing to hummingbirds. Its vibrant blooms, specialized floral structure, and ecological timing ensure it remains a favorite among these pollinators.
- Bright Red and Yellow Flowers
The striking red and yellow coloration of Eastern Red Columbine’s flowers is one of its most defining features. Hummingbirds are naturally drawn to bright colors, particularly red, which signals a rich nectar source. The nodding flowers stand out in woodland or garden settings, making them easy for hummingbirds to locate.
- Talon-Shaped Spurs
The flowers of Eastern Red Columbine feature elongated, tubular spurs filled with sweet nectar. These spurs are perfectly adapted to the long bills and tongues of hummingbirds, allowing them to access nectar deep within the flower. As hummingbirds feed, they inadvertently collect pollen on their heads and transfer it between flowers, ensuring successful pollination.
- High Nectar Content
Eastern Red Columbine produces nectar with a high sugar concentration, providing hummingbirds with the energy they need for their rapid flight and high metabolism. The nectar’s sugar content is notably higher than many other wildflowers, making it an essential food source during the birds’ migration period.
- Seasonal Synchronization
The blooming period of Eastern Red Columbine (March–May) coincides with the return of migrating Ruby-throated Hummingbirds in early spring. This co-evolution ensures that hummingbirds have access to abundant nectar just when they need it most after their long journey north.
- Adaptability
Eastern Red Columbine thrives in various conditions, from rocky woodlands to shaded gardens. Its ability to self-seed allows it to form large colonies over time, creating dense feeding grounds for hummingbirds.
With its vibrant flowers, specialized spurs, and high nectar production, Eastern Red Columbine is a vital plant for attracting hummingbirds while supporting pollinator health in native ecosystems.
2. Wild Geranium (Geranium maculatum)
Wild Geranium (Geranium maculatum), also known as Spotted Cranesbill, is a charming perennial wildflower native to the Eastern United  States. Renowned for its delicate beauty and ecological benefits, this plant is an excellent choice for gardens that aim to attract hummingbirds, butterflies, and other pollinators.
States. Renowned for its delicate beauty and ecological benefits, this plant is an excellent choice for gardens that aim to attract hummingbirds, butterflies, and other pollinators.
Key Characteristics
-
Zones: 3–8
-
Height: 1–2 feet
-
Bloom Time: April–June
-
Features: Clusters of pink to lavender five-petaled flowers atop slender stems, complemented by deeply lobed green foliage.
The soft, pastel blooms of Wild Geranium are a welcome sight in spring gardens, providing nectar for hummingbirds as they return from migration. Its flowers are particularly attractive to pollinators due to their open structure, which offers easy access to nectar and pollen.
Natural Habitat
Wild Geranium thrives in woodland settings, shaded meadows, and forest edges. It prefers rich, moist soils but can tolerate drier conditions once  established. Its adaptability makes it a versatile addition to various garden types, from shaded borders to naturalized areas.
established. Its adaptability makes it a versatile addition to various garden types, from shaded borders to naturalized areas.
Care and Maintenance
This low-maintenance plant is ideal for gardeners seeking beauty without extensive upkeep. Wild Geranium grows well in partial shade but can handle full sun in cooler climates. To keep the plant healthy:
-
Ensure the soil remains moderately moist but well-drained.
-
Remove spent blooms to encourage fresh flowering and prevent self-seeding if desired.
-
Divide mature plants every few years to maintain vigor and control spreading.
Ecological Benefits
Wild Geranium plays a vital role in supporting local ecosystems. Its nectar-rich flowers attract hummingbirds and native bees, while its foliage provides shelter for small insects. The plant’s ability to naturalize also helps stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
Garden Uses
Wild Geranium is a versatile addition to:
-
Shade Gardens: Brighten up darker areas with its colorful blooms.
-
Pollinator Gardens: Provide nectar for hummingbirds during their active spring season.
-
Woodland Gardens: Complement native ferns and groundcovers with its elegant flowers.
-
Borders and Edges: Add soft texture and color to garden perimeters.
Why Choose Wild Geranium?
With its effortless charm, ecological importance, and adaptability, Wild Geranium is a must-have for gardeners looking to support pollinators while enhancing their landscapes. Whether planted in shaded corners or sunny edges, this native wildflower will thrive and delight year after year.
Wild Geranium (Geranium maculatum), also known as Spotted Cranesbill, is a charming perennial wildflower native to the Eastern United States. Renowned for its delicate beauty and ecological benefits, this plant is an excellent choice for gardens that aim to attract hummingbirds, butterflies, and other pollinators.
How does Wild Geranium attract hummingbirds
Wild Geranium (Geranium maculatum) attracts hummingbirds through its nectar-rich flowers and its ability to create a thriving ecosystem for pollinators. While the blooms of Wild Geranium are not tubular like many classic hummingbird-attracting flowers, they are filled with an abundance of sweet nectar that hummingbirds find irresistible. The plant’s lavender to pink flowers bloom in clusters during the spring and early summer, providing a vital food source for these birds as they return from migration.
The flowers’ open, cup-shaped design allows easy access to nectar, accommodating the long beaks of hummingbirds. Additionally, the plant’s vibrant blooms stand out in woodland or shaded garden settings, making it easier for hummingbirds to locate. Planting Wild Geranium in dense clusters further enhances its appeal by creating a visually prominent and abundant feeding area.
Beyond its nectar, Wild Geranium indirectly attracts hummingbirds by drawing in insects such as ants, beetles, and syrphid flies. Hummingbirds rely on these insects as a protein source, especially during nesting season. By supporting a diverse insect population, Wild Geranium becomes an essential part of the food web in a pollinator-friendly garden.
This native perennial is also easy to grow and maintain, thriving in partial shade to full sun and tolerating a variety of soil conditions. Its adaptability and ecological benefits make it an excellent choice for gardeners looking to support wildlife. Whether planted in shaded borders, woodland gardens, or naturalized areas, Wild Geranium not only enhances the beauty of your
3. Coral Honeysuckle (Lonicera sempervirens): A Hummingbird Magnet for Your Garden
Coral Honeysuckle (Lonicera sempervirens) is a stunning native vine that not only adds vibrant color to your landscape but also serves as a  magnet for hummingbirds. This perennial climbing plant, known for its tubular red flowers and yellow interiors, is a favorite nectar source for these energetic birds. Its long bloom period and ecological benefits make it an excellent addition to any garden in the Eastern United States.
magnet for hummingbirds. This perennial climbing plant, known for its tubular red flowers and yellow interiors, is a favorite nectar source for these energetic birds. Its long bloom period and ecological benefits make it an excellent addition to any garden in the Eastern United States.
Key Characteristics
-
Zones: 4–9
-
Height: Up to 20 feet (with support)
-
Bloom Time: March–July, with sporadic blooms into fall
-
Features: Clusters of trumpet-shaped red flowers followed by small red berries.
The vivid red blooms of Coral Honeysuckle are perfectly adapted to attract hummingbirds. Their tubular shape fits the long bills of these birds, allowing easy access to nectar. The bright coloration also acts as a visual beacon, drawing hummingbirds from afar.
Natural Habitat
Coral Honeysuckle thrives in woodlands, along fences, and on rocky slopes. It is well-suited to sunny or partially shaded areas and prefers moist, well-drained soil. Unlike invasive honeysuckle species, this native vine is non-aggressive and integrates harmoniously into the landscape.
Care and Maintenance
This low-maintenance plant is ideal for gardeners who want beauty without constant upkeep. To grow Coral Honeysuckle successfully:
-
Provide a trellis, fence, or arbor for support.
-
Plant it in full sun for the best flowering, though it tolerates partial shade.
-
Prune lightly after flowering to encourage new growth and maintain shape.
Ecological Benefits
In addition to attracting hummingbirds, Coral Honeysuckle supports other pollinators like butterflies and bees. Its red berries feed songbirds in late summer and fall, making it a valuable food source for wildlife.
Why Choose Coral Honeysuckle?
Coral Honeysuckle is a versatile, show-stopping vine that brings life and color to your garden while supporting local ecosystems. Whether adorning an arbor or climbing along a fence, this native plant will delight gardeners and hummingbirds alike year after year.
Unique Characteristics of Coral Honeysuckle That Attract Hummingbirds
Coral Honeysuckle (Lonicera sempervirens), often referred to as the “hummingbird vine,” is a native plant renowned for its ability to attract hummingbirds. Its unique features make it a vital addition to gardens designed to support these iconic pollinators.
- Brightly Colored Tubular Flowers
The most distinctive characteristic of Coral Honeysuckle is its long, tubular flowers, which range in color from vibrant red to orange and  occasionally yellow. These bright hues are highly attractive to hummingbirds, as they are drawn to red and other warm tones. The tubular shape of the flowers perfectly matches the long bills of hummingbirds, allowing them easy access to nectar while excluding most insects, ensuring the nectar remains available for the birds.
occasionally yellow. These bright hues are highly attractive to hummingbirds, as they are drawn to red and other warm tones. The tubular shape of the flowers perfectly matches the long bills of hummingbirds, allowing them easy access to nectar while excluding most insects, ensuring the nectar remains available for the birds.
- Abundant Nectar Production
Coral Honeysuckle’s flowers are rich in nectar, making them an essential energy source for hummingbirds. The plant blooms prolifically in mid-spring—coinciding with the arrival of hummingbirds from their migration—and continues to flower sporadically throughout the summer. This extended bloom period provides a reliable food supply over several months.
- Co-Evolution with Hummingbirds
The flower structure and nectar availability suggest Coral Honeysuckle has co-evolved with hummingbirds. Its slender tubes are tailored to accommodate their feeding habits, making it one of the most efficient plants for supporting these birds.
- Easy Visibility
Clusters of flowers appear at the ends of vines, creating prominent feeding spots that hummingbirds can easily locate. Planting Coral Honeysuckle on trellises or fences enhances its visibility, further enticing hummingbirds.
- Additional Benefits
Beyond attracting hummingbirds, Coral Honeysuckle supports butterflies and bees while producing red berries that feed songbirds in late summer. Its ecological versatility makes it a valuable addition to any wildlife-friendly garden.
By incorporating Coral Honeysuckle into your landscape, you can create a vibrant and sustainable habitat that ensures hummingbirds return year after year.
Summer Bloomers
Summer is a time of abundance, with many native plants providing nectar during the peak activity of hummingbirds.
4. Cardinal Flower (Lobelia cardinalis): A Striking Magnet for Hummingbirds
The Cardinal Flower (Lobelia cardinalis) is one of the most stunning native plants in the Eastern United States, renowned for its vibrant red  blooms and its ability to attract hummingbirds. This perennial wildflower is a must-have for gardeners looking to create a pollinator-friendly landscape while adding a dramatic splash of color to their gardens.
blooms and its ability to attract hummingbirds. This perennial wildflower is a must-have for gardeners looking to create a pollinator-friendly landscape while adding a dramatic splash of color to their gardens.
Key Characteristics
-
Zones: 2–9
-
Height: 3–4 feet
-
Bloom Time: July–September
-
Features: Tall spikes of bright scarlet, tubular flowers that stand out against lush green foliage.
The Cardinal Flower’s brilliant red flowers are specifically designed to attract hummingbirds. Its tubular blooms are perfectly shaped for the long bills and tongues of these birds, ensuring easy access to its nectar. The bold red color is also highly visible to hummingbirds, who are naturally drawn to bright hues.
Natural Habitat
Cardinal Flowers thrive in moist environments such as stream banks, wetlands, and woodland edges. They prefer rich, consistently damp soil but can adapt to garden settings when provided with adequate moisture. Their natural habitat makes them an excellent choice for rain gardens or areas with poor drainage.
Care and Maintenance
While Cardinal Flowers require slightly more attention than some other native plants, they reward gardeners with spectacular blooms. To grow  them successfully:
them successfully:
-
Plant in full sun to partial shade.
-
Keep the soil consistently moist, especially during hot or dry periods.
-
Mulch around the base to retain moisture and prevent weeds.
-
Allow plants to reseed naturally for continuous growth year after year.
Ecological Benefits
The Cardinal Flower is a powerhouse for pollinators. Its nectar-rich flowers are a favorite of hummingbirds, while butterflies and bees also benefit from its blooms. Additionally, it supports biodiversity by providing habitat for insects and small wildlife.
Why Choose Cardinal Flower?
The Cardinal Flower’s striking beauty and ecological importance make it an essential addition to any garden. Whether planted in borders, near water features, or in pollinator gardens, this native wildflower will captivate gardeners and hummingbirds alike while enhancing the health of local ecosystems.
What are the unique characteristics of Cardinal Flower that make it attractive to hummingbirds
Cardinal Flower (Lobelia cardinalis) is a standout native plant for attracting hummingbirds, thanks to its vibrant red blooms and specialized  floral structure. This perennial wildflower has evolved unique traits that make it particularly appealing to these energetic pollinators.
floral structure. This perennial wildflower has evolved unique traits that make it particularly appealing to these energetic pollinators.
- Vivid Red Color
The Cardinal Flower’s striking scarlet blossoms are one of its most defining features. Hummingbirds are naturally drawn to bright red hues, which signal a rich nectar source. The flowers’ intense coloration makes them highly visible to hummingbirds from a distance, ensuring the plant stands out even in dense vegetation.
- Tubular Flower Shape
The tubular structure of Cardinal Flower’s blooms is perfectly adapted to the long bills and tongues of hummingbirds. This design allows hummingbirds to easily access nectar deep within the flower while minimizing competition from other pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, which are less suited to the flower’s shape.
- High Nectar Production
Cardinal Flowers produce abundant nectar, a crucial energy source for hummingbirds. The plant’s bloom period, which lasts from midsummer to early fall, coincides with the time when hummingbirds are preparing for their southward migration. This makes it an essential food source during their most active feeding period.
- Sequential Blooming
The flowers on the tall spikes of Cardinal Flower open sequentially from bottom to top. This staggered blooming ensures a continuous supply of nectar over several weeks, keeping hummingbirds returning to the plant throughout its flowering season.
- Adaptability to Moist Environments
Cardinal Flower thrives in wet habitats such as stream banks, rain gardens, and wetlands—areas where hummingbirds often forage. Its ability to grow in shady or partially shaded spots also makes it accessible in diverse garden settings.
- Pollination Partnership
Hummingbirds play a crucial role in pollinating Cardinal Flowers. As they sip nectar, pollen is deposited on their heads and transferred between flowers, ensuring successful reproduction. This symbiotic relationship highlights the plant’s reliance on hummingbirds for survival.
With its brilliant color, abundant nectar, and specialized floral design, Cardinal Flower is perfectly suited for attracting hummingbirds while enhancing any garden with its dramatic beauty.
5. Bee Balm (Monarda didyma): A Vibrant Favorite for Hummingbirds
Bee Balm (Monarda didyma), also known as Scarlet Beebalm or Oswego Tea, is a native perennial that brings vibrant color and life to gardens  across the Eastern United States. Known for its striking red, pink, or purple flowers, this plant is a magnet for hummingbirds, butterflies, and bees. Its beauty and ecological benefits make it a must-have for pollinator-friendly landscapes.
across the Eastern United States. Known for its striking red, pink, or purple flowers, this plant is a magnet for hummingbirds, butterflies, and bees. Its beauty and ecological benefits make it a must-have for pollinator-friendly landscapes.
Key Characteristics
-
Zones: 4–9
-
Height: 2–4 feet
-
Bloom Time: June–August
-
Features: Dense clusters of tubular flowers atop square stems with aromatic, mint-like foliage.
The bright, tubular blooms of Bee Balm are perfectly designed to attract hummingbirds. The flowers’ shape allows these birds to easily access the nectar while their vibrant colors act as a visual beacon. Bee Balm’s long bloom period ensures a consistent food source during the height of summer when hummingbirds are most active.
Natural Habitat
Bee Balm thrives in moist meadows, woodland edges, and along stream banks. It prefers rich, well-drained soil and full sun but can tolerate partial shade. Its ability to naturalize makes it an excellent choice for wildflower gardens or naturalized areas.
Care and Maintenance
Bee Balm is relatively low-maintenance but benefits from proper care:
-
Plant in full sun for optimal flowering.
-
Keep soil consistently moist but well-drained.
-
Thin plants regularly to improve air circulation and prevent powdery mildew.
-
Deadhead spent blooms to encourage continuous flowering.
Ecological Benefits
Bee Balm is a powerhouse for pollinators. Its nectar-rich flowers are a favorite of hummingbirds, while butterflies and native bees also benefit from its blooms. Additionally, its aromatic foliage deters deer and other garden pests.
Why Choose Bee Balm?
With its stunning appearance, ease of care, and ability to support pollinators, Bee Balm is an essential addition to any garden. Whether planted in borders, pollinator gardens, or naturalized spaces, this native wildflower will attract hummingbirds and add vibrant beauty to your landscape year after year.
What are the unique characteristics of Bee Balm that attract hummingbirds
Bee Balm (Monarda didyma) is a standout native plant for attracting hummingbirds, thanks to its vibrant blooms and specialized floral  features. This perennial wildflower offers a combination of traits that make it irresistible to these energetic pollinators.
features. This perennial wildflower offers a combination of traits that make it irresistible to these energetic pollinators.
- Bright, Vibrant Colors
Bee Balm blooms in striking shades of red, pink, purple, and sometimes white. Hummingbirds are naturally drawn to bright colors, particularly red, as they signal a rich nectar source. The vivid hues of Bee Balm make it easy for hummingbirds to spot from a distance, ensuring the plant stands out in any garden.
- Tubular Flower Structure
The tubular shape of Bee Balm’s flowers is perfectly suited to the long bills and tongues of hummingbirds. This design allows them to access nectar deep within the flower while minimizing competition from other pollinators like bees and butterflies. The flowers are held in dense clusters at the top of their stems, creating convenient feeding stations for hummingbirds.
- Abundant Nectar Production
Bee Balm is known for its high nectar output, making it one of the most reliable food sources for hummingbirds during their active summer months. Its long bloom period, typically from June to August, ensures a steady supply of nourishment throughout the season.
- Continuous Blooming
With proper care, such as deadheading spent flowers, Bee Balm can produce successive blooms throughout the summer. This extended flowering period provides hummingbirds with consistent access to nectar over several weeks.
- Aromatic Foliage
Bee Balm’s mint-scented foliage adds another layer of appeal. While not directly attracting hummingbirds, its fragrance deters deer and other pests, ensuring the flowers remain undisturbed for pollinators.
- Adaptability
Bee Balm thrives in sunny locations with moist but well-drained soil. Its ability to grow in diverse conditions makes it accessible in both small spaces and large pollinator gardens.
With its vibrant colors, tubular flowers, and abundant nectar production, Bee Balm is a top choice for gardeners looking to attract hummingbirds while enhancing their landscape with bold beauty.
6. Jewelweed (Impatiens capensis): A Natural Hummingbird Favorite
Jewelweed (Impatiens capensis), also known as Spotted Touch-Me-Not, is a vibrant native wildflower that thrives in moist, shaded areas  across the Eastern United States. Renowned for its bright orange, trumpet-shaped flowers, this plant is a favorite among hummingbirds and an essential addition to pollinator-friendly gardens.
across the Eastern United States. Renowned for its bright orange, trumpet-shaped flowers, this plant is a favorite among hummingbirds and an essential addition to pollinator-friendly gardens.
Key Characteristics
-
Zones: 2–11
-
Height: 2–5 feet
-
Bloom Time: July–October
-
Features: Bright orange flowers with red spots and a tubular shape, paired with succulent, light-green stems.
The unique structure of Jewelweed’s flowers is perfectly adapted to attract hummingbirds. Its tubular blooms are an ideal fit for their long bills and tongues, allowing them to access the plant’s abundant nectar. The vibrant orange color is another key feature that draws hummingbirds, as they are naturally attracted to warm tones.
Natural Habitat
Jewelweed thrives in damp environments such as stream banks, wetlands, and forest edges. It prefers partial to full shade and moist soil, making it an excellent choice for rain gardens or naturalized areas with poor drainage. In the wild, it often grows in dense colonies, creating a rich feeding ground for pollinators.
Care and Maintenance
Jewelweed is a self-sufficient plant that requires minimal care:
-
Plant it in moist, shaded areas with rich soil.
-
Allow it to self-seed naturally; its explosive seed pods ensure new plants will grow each year.
-
Avoid overwatering in already damp conditions.
Ecological Benefits
Jewelweed supports not only hummingbirds but also butterflies and bees. Additionally, it provides habitat for insects and its seeds are a food source for birds. The plant’s ability to outcompete invasive species like garlic mustard makes it ecologically valuable.
Why Choose Jewelweed?
With its vibrant flowers, ecological importance, and ability to thrive in challenging conditions, Jewelweed is an excellent choice for gardeners looking to attract hummingbirds while supporting native ecosystems. Its beauty and resilience make it a standout addition to any shade garden or wetland area.
What are the unique characteristics of Jewelweed that attract hummingbirds
Jewelweed (Impatiens capensis), also known as Spotted Touch-Me-Not, is a native annual wildflower with several unique traits that make it highly appealing to hummingbirds. Its vibrant flowers, nectar-rich blooms, and ecological timing ensure it plays a vital role in supporting these pollinators.
- Bright Orange Flowers
Jewelweed produces striking orange flowers with red spots, which are highly visible to hummingbirds. The bright coloration acts as a visual cue,  making the plant easy to locate in shaded or wet areas. Hummingbirds are naturally drawn to warm colors like orange and red, which signal a reliable nectar source.
making the plant easy to locate in shaded or wet areas. Hummingbirds are naturally drawn to warm colors like orange and red, which signal a reliable nectar source.
- Tubular Nectar Spurs
The flowers of Jewelweed feature curved, tubular spurs filled with nectar. These spurs are perfectly adapted to the long bills and tongues of hummingbirds, allowing them to access nectar deep within the flower. The unique structure ensures efficient pollination, as hummingbirds transfer pollen between flowers while feeding.
- High Sugar Content in Nectar
Jewelweed’s nectar is exceptionally rich in sugar, with concentrations reaching up to 40%. This is significantly higher than the nectar produced by many other plants (typically 20–33%), making it an energy-dense food source for hummingbirds. The high sugar content is particularly beneficial during migration when hummingbirds need to build energy reserves.
- Seasonal Blooming
Jewelweed blooms from late summer through fall, coinciding with the southward migration of Ruby-throated Hummingbirds. This synchronization ensures that Jewelweed serves as a critical food source when other nectar plants have finished flowering.
- Dense Colonies
Jewelweed often grows in large patches in damp environments like stream banks and wetlands. These dense colonies provide hummingbirds with abundant feeding opportunities, reducing their reliance on artificial feeders.
With its vivid flowers, specialized spurs, and high-sugar nectar, Jewelweed is an essential native plant for attracting hummingbirds while supporting their migration and overall health.
7. Fire Pink (Silene virginica): A Fiery Beauty for Hummingbirds
Fire Pink (Silene virginica) is a striking native wildflower that brings vibrant color and ecological value to gardens and natural landscapes.  Known for its brilliant red, star-shaped flowers, this perennial plant is a favorite among hummingbirds, making it an excellent choice for pollinator-friendly gardens in the Eastern United States.
Known for its brilliant red, star-shaped flowers, this perennial plant is a favorite among hummingbirds, making it an excellent choice for pollinator-friendly gardens in the Eastern United States.
Key Characteristics
-
Zones: 4–8
-
Height: Up to 1 foot
-
Bloom Time: May–July
-
Features: Bright red, five-petaled flowers with a delicate fringe, held on slender stems above basal rosettes of green leaves.
The vivid red blooms of Fire Pink are highly attractive to hummingbirds, who are naturally drawn to bright colors. The flower’s tubular shape and open structure make it easy for hummingbirds to access the nectar deep within. This plant’s fiery appearance not only adds visual interest to your garden but also creates an essential feeding station for these energetic birds.
Natural Habitat
Fire Pink thrives in rocky woodlands, open meadows, and along forest edges. It prefers well-drained soil and sunny to partially shaded conditions. Its natural ability to grow in challenging environments, such as rocky slopes or poor soils, makes it an adaptable addition to gardens.
Care and Maintenance
Fire Pink is relatively low-maintenance but benefits from proper care:
-
Plant in well-drained soil with good sun exposure.
-
Avoid overwatering; the plant is drought-tolerant once established.
-
Deadhead spent blooms to encourage prolonged flowering and prevent self-seeding if desired.
Ecological Benefits
Fire Pink’s nectar-rich flowers are perfectly suited for hummingbirds, which are its primary pollinators. The plant’s bright blooms also attract butterflies and other pollinators, supporting biodiversity in your garden.
Why Choose Fire Pink?
With its stunning red flowers, ease of care, and ability to attract hummingbirds, Fire Pink is a standout choice for gardeners looking to enhance their landscapes while supporting native wildlife. Whether planted in rock gardens, woodland edges, or sunny borders, this fiery wildflower will bring life and color to your garden year after year.
What are the unique characteristics of Fire Pink that attract hummingbirds
Fire Pink (Silene virginica) is a native perennial wildflower with several unique traits that make it highly appealing to hummingbirds. Its vibrant blooms, specialized floral structure, and ecological adaptations ensure it remains a favorite among these pollinators.
- Brilliant Scarlet Flowers
The striking scarlet-red color of Fire Pink’s flowers is one of its most eye-catching features. Hummingbirds are naturally drawn to bright colors  like red, which signal a rich nectar source. The vivid blooms stand out in woodland edges, meadows, and rocky slopes, making them easy for hummingbirds to locate.
like red, which signal a rich nectar source. The vivid blooms stand out in woodland edges, meadows, and rocky slopes, making them easy for hummingbirds to locate.
- Tubular Flower Shape
The flowers of Fire Pink have a narrow tubular structure that is perfectly suited to the long bills and tongues of hummingbirds. This design allows hummingbirds to access nectar deep within the flower while minimizing competition from other pollinators, such as bees and butterflies.
- High Nectar Production
Fire Pink produces abundant nectar, making it an energy-rich food source for hummingbirds. Its blooming period, which lasts from late spring through early summer (April–July), aligns with the active feeding season of Ruby-throated Hummingbirds, ensuring they have access to nourishment during critical times.
- Sticky-Hairy Stems
The plant’s sticky hairs on its stems and calyx act as natural flypaper, deterring ants and small insects from stealing nectar. This adaptation ensures that larger pollinators like hummingbirds can access the nectar without interference.
- Adaptability to Rocky and Dry Soils
Fire Pink thrives in challenging environments such as rocky slopes and dry woodlands. Its ability to grow in well-drained soil with partial sun makes it a versatile addition to gardens designed for pollinators.
With its vivid blooms, tubular flowers, and high nectar output, Fire Pink is an essential plant for attracting hummingbirds while adding striking beauty to naturalized landscapes or pollinator-friendly gardens.
Fall Bloomers
Fall-blooming plants provide critical nectar as hummingbirds prepare for their southward migration.
8. Butterfly Weed (Asclepias tuberosa): A Vibrant Nectar Source for Hummingbirds
Butterfly Weed (Asclepias tuberosa) is a stunning native perennial that brings vibrant orange blooms and ecological benefits to gardens across

the Eastern United States. While it is best known for supporting butterflies, particularly monarchs, this hardy plant is also a favorite of hummingbirds, thanks to its abundant nectar and bright flowers.
Key Characteristics
-
Zones: 3–10
-
Height: 1–3 feet
-
Bloom Time: June–August
-
Features: Clusters of fiery orange, star-shaped flowers atop sturdy stems with narrow, lance-shaped leaves.
The vivid orange flowers of Butterfly Weed are highly attractive to hummingbirds. The bright color acts as a visual signal, drawing them in from a distance. Its small, tubular blooms are perfectly designed to accommodate the long bills and tongues of hummingbirds, allowing them to access the nectar deep within.
Natural Habitat
Butterfly Weed thrives in sunny meadows, prairies, and along roadsides. It prefers well-drained soil and tolerates dry conditions, making it an excellent choice for xeriscaping or low-maintenance gardens. Its deep taproot allows it to survive in challenging environments, such as rocky or sandy soils.
Care and Maintenance
Butterfly Weed is easy to grow and requires minimal care:
-
Plant in full sun for optimal flowering.
-
Avoid overwatering; it thrives in dry to moderately moist soil.
-
Allow the plant to reseed naturally or collect seeds for propagation.
-
Avoid transplanting mature plants due to their deep taproots.
Ecological Benefits
In addition to attracting hummingbirds with its nectar-rich blooms, Butterfly Weed supports butterflies, bees, and other pollinators. It serves as a host plant for monarch butterfly caterpillars and produces seeds with silky fibers that aid in wind dispersal.
Why Choose Butterfly Weed?
With its vibrant flowers, ease of care, and ability to attract both hummingbirds and butterflies, Butterfly Weed is a standout addition to any pollinator-friendly garden. Its brilliant color and ecological importance make it a must-have for gardeners looking to support wildlife while adding natural beauty to their landscapes.
Ecological Benefits
In addition to attracting hummingbirds, Butterfly Weed supports butterflies, bees, and other pollinators. It also serves as a host plant for monarch butterfly caterpillars, further enhancing its ecological importance.
With its vibrant color, specialized flower structure, and high nectar output, Butterfly Weed is
a must-have plant for gardeners looking to attract hummingbirds while supporting native ecosystems.
What are the unique characteristics of Butterfly Weed that make it attractive to hummingbirds
Butterfly Weed (Asclepias tuberosa) is a vibrant perennial wildflower with several unique traits that make it highly appealing to  hummingbirds. Its combination of bright colors, abundant nectar, and adaptability ensures it stands out as a reliable food source for these pollinators.
hummingbirds. Its combination of bright colors, abundant nectar, and adaptability ensures it stands out as a reliable food source for these pollinators.
- Bright, Eye-Catching Flowers
The vivid orange to orange-yellow blooms of Butterfly Weed are one of its most striking features. Hummingbirds are naturally drawn to warm colors like orange and red, which signal a rich nectar source. The flat-topped clusters of flowers provide a prominent visual cue, making the plant easy for hummingbirds to locate.
- Tubular Flower Design
Each flower in the cluster has a tubular structure with reflexed petals and a crown-like center. This design is perfectly suited to the long bills and tongues of hummingbirds, allowing them to access nectar deep within the flower while minimizing competition from other pollinators.
- Abundant Nectar Production
Butterfly Weed produces copious amounts of nectar, making it an energy-rich food source for hummingbirds. Its long bloom period, lasting from late spring through summer, ensures a consistent supply of nectar during the peak feeding season for these birds.
- Adaptability to Dry Conditions
Hummingbirds often forage in open, sunny areas, and Butterfly Weed thrives in such environments. Its deep taproot allows it to grow in dry, well-drained soils, ensuring it continues to provide nectar even during droughts when other plants may struggle.
- Ecological Benefits
In addition to attracting hummingbirds, Butterfly Weed supports butterflies, bees, and other pollinators. It serves as a host plant for monarch butterfly caterpillars and produces seed pods that aid in wind dispersal.
With its brilliant blooms, specialized flower structure, and high nectar output, Butterfly Weed is an essential addition to gardens designed to attract hummingbirds while supporting native ecosystems.
9. Goldenrod (Solidago spp.): A Late-Season Nectar Source for Hummingbirds
Goldenrod (Solidago spp.) is a native perennial wildflower that lights up gardens and natural landscapes with its golden-yellow blooms in late  What are the unique characteristics of Goldenrod that make it attractive to hummingbirdssummer and fall. While often associated with supporting bees and butterflies, Goldenrod also plays a key role in attracting hummingbirds during their critical migration period. Its ecological benefits and striking appearance make it a valuable addition to pollinator-friendly gardens.
What are the unique characteristics of Goldenrod that make it attractive to hummingbirdssummer and fall. While often associated with supporting bees and butterflies, Goldenrod also plays a key role in attracting hummingbirds during their critical migration period. Its ecological benefits and striking appearance make it a valuable addition to pollinator-friendly gardens.
Key Characteristics
-
Zones: 3–9
-
Height: 1–5 feet
-
Bloom Time: August–October
-
Features: Dense clusters of tiny, bright yellow flowers atop tall stems with narrow, lance-shaped leaves.
Goldenrod’s abundant blooms provide nectar late in the growing season when many other plants have finished flowering. This makes it an essential food source for hummingbirds as they prepare for their southward migration, helping them build the energy reserves needed for the long journey.
Natural Habitat
Goldenrod thrives in a variety of environments, including meadows, prairies, roadsides, and woodland edges. It prefers full sun and well-drained soil but can tolerate partial shade and less-than-ideal conditions, making it highly adaptable to different garden settings.
Care and Maintenance
Goldenrod is easy to grow and requires minimal care:
-
Plant in full sun for optimal flowering.
-
Choose well-drained soil, but avoid over-fertilizing as this can lead to aggressive growth.
-
Thin plants periodically to prevent overcrowding.
-
Cut back stems after flowering to encourage tidy growth.
Ecological Benefits
Goldenrod supports hummingbirds by providing nectar during their migration. It also attracts bees, butterflies, and other pollinators while serving as a host plant for certain caterpillars. Additionally, its seeds feed small birds in late fall.
Why Choose Goldenrod?
With its vibrant flowers, late-season blooms, and ability to attract hummingbirds alongside other pollinators, Goldenrod is an essential addition to any wildlife-friendly garden. Its resilience and ecological importance make it a standout choice for gardeners looking to enhance their landscapes while supporting native ecosystems.
What are the unique characteristics of Goldenrod that make it attractive to hummingbirds
Goldenrod (Solidago spp.) is a native wildflower with several distinctive traits that make it appealing to hummingbirds, especially during their late-season feeding and migration periods. Its vibrant blooms, nectar-rich flowers, and adaptability contribute to its role as a valuable food source for these pollinators.
- Bright Yellow Blooms
Goldenrod’s dense clusters of golden-yellow flowers are one of its most recognizable features. While hummingbirds are typically drawn to red and orange hues, they also visit yellow flowers when nectar is abundant. The bright color of Goldenrod’s blooms acts as a visual cue, making it easy for hummingbirds to locate the plant in open meadows or along woodland edges.
Abundant Nectar Supply
Goldenrod produces copious amounts of nectar, particularly in warm weather or when soil moisture is sufficient. This makes it an important energy source for hummingbirds during late summer and fall (August–October), a critical time when they are building reserves for their southward migration.
- Late-Season Blooming
Unlike many other wildflowers that finish blooming by midsummer, Goldenrod flowers persist into the fall. This extended bloom period ensures  that hummingbirds have access to nectar when other plants are no longer flowering, making it a crucial resource during the changing seasons.
that hummingbirds have access to nectar when other plants are no longer flowering, making it a crucial resource during the changing seasons.
- Adaptability to Diverse Habitats
Goldenrod thrives in a wide range of environments, from sunny meadows and prairies to woodland edges and roadsides. Its ability to grow in various soil types, including dry or poor soils, ensures that it can provide nectar in habitats where other plants may struggle.
- Support for Ecosystems
While attracting hummingbirds with its nectar, Goldenrod also supports bees, butterflies, and other pollinators. Its seeds provide food for birds like finches and sparrows, while its foliage and stems host caterpillars and beneficial insects.
With its vibrant blooms, high nectar production, and ecological versatility, Goldenrod is an essential plant for supporting hummingbirds and other wildlife in late-season gardens or natural landscapes.
10. Autumn Sage (Salvia greggii): A Year-Round Delight for Hummingbirds
Autumn Sage (Salvia greggii) is a versatile, drought-tolerant perennial that brings vibrant color and life to gardens. Known for its tubular flowers and long blooming period, this plant is a hummingbird magnet, making it a favorite among gardeners who want to support pollinators while enhancing their landscapes.
Key Characteristics
-
Zones: 6–9
-
Height: 2–3 feet
-
Bloom Time: Late spring to fall, with sporadic blooms year-round in warmer climates.
-
Features: Tubular flowers in shades of red, pink, coral, or white that grow on upright stems with aromatic, semi-evergreen foliage.
The bright red and coral hues of Autumn Sage are particularly attractive to hummingbirds, as they are naturally drawn to warm colors. The tubular shape of the flowers is perfectly suited to the long bills and tongues of hummingbirds, allowing them to access nectar deep within the blooms.
Natural Habitat
Native to the arid regions of Texas and Mexico, Autumn Sage thrives in dry, well-drained soil and full sun. Its adaptability makes it an excellent choice for xeriscaping or low-maintenance gardens. It also works well in containers, borders, or pollinator gardens.
Care and Maintenance
Autumn Sage is low-maintenance and easy to grow:
-
Plant in full sun for optimal flowering.
-
Water sparingly; it is drought-tolerant once established.
-
Prune lightly after flowering to encourage new growth and maintain shape.
-
Mulch around the base to retain moisture in hot climates.
Ecological Benefits
Autumn Sage provides abundant nectar for hummingbirds throughout its long blooming season. It also attracts butterflies and bees while deterring deer with its aromatic foliage.
Why Choose Autumn Sage?
With its vibrant flowers, extended bloom time, and ability to thrive in tough conditions, Autumn Sage is an essential addition to any hummingbird-friendly garden. Its beauty and resilience make it a standout plant for supporting pollinators while adding year-round interest to your landscape.
What are the unique characteristics of Autumn Sage that make it attractive to hummingbirds
Autumn Sage (Salvia greggii) is one of the most effective plants for attracting hummingbirds, thanks to its vibrant flowers, extended bloom period, and specialized floral structure. Its adaptability and ecological benefits make it a favorite among gardeners and pollinators alike.
- Bright, Tubular Flowers
The tubular shape of Autumn Sage’s flowers is perfectly suited to the long bills and tongues of hummingbirds. This design allows them to easily access nectar deep within the blooms. The flowers come in a variety of colors, including red, pink, coral, purple, and white, with red being particularly attractive to hummingbirds due to their preference for warm hues.
- Abundant Nectar Production
Autumn Sage produces nectar-rich blooms that provide a reliable food source for hummingbirds. Its flowers are designed to maximize nectar accessibility while ensuring efficient pollen transfer during feeding. The high nectar content makes it a critical energy source for these birds.
- Extended Bloom Period
One of the standout features of Autumn Sage is its long blooming season, which lasts from spring through fall and sometimes year-round in warmer climates. This ensures that hummingbirds have access to nectar over an extended period, particularly during migration when their energy demands are highest.
- Compact Size and Visibility
Autumn Sage grows as a small shrub (up to 3 feet tall), making its blooms highly visible and accessible to hummingbirds. Its dense clusters of flowers create concentrated feeding areas that attract multiple birds at once.
- Adaptability
Native to arid regions like Texas and Mexico, Autumn Sage thrives in sunny locations with well-drained soil. Its drought tolerance ensures that it continues to provide nectar even in dry conditions, making it ideal for low-water gardens.
With its vibrant colors, abundant nectar, and extended blooming period, Autumn Sage is an essential addition to any garden designed to attract hummingbirds while supporting pollinator health year-round.
Additional Plants Worth Considering
Expand your garden’s diversity with these additional native options:
-
*Copper Iris (Iris fulva): Moisture-loving perennial with coppery-red blooms.
-
*Royal Catchfly (Silene regia): Tall stems with brilliant red flowers.
-
*Purple Coneflower (Echinacea purpurea): Long-lasting pink blooms that attract both hummingbirds and butterflies.
-
*Wild Bergamot (Monarda fistulosa): Lavender blooms that thrive in sunny meadows.
-
*Swamp Milkweed (Asclepias incarnata): Pink clusters perfect for damp areas.
-
*Foxglove Beard Tongue (Penstemon digitalis): White tubular flowers that bloom early summer.
-
*Garden Phlox (Phlox paniculata): Fragrant pink or purple blossoms loved by pollinators.
Designing Your Hummingbird Garden
Creating a garden tailored for hummingbirds involves thoughtful planning:
-
Select plants with staggered bloom times to ensure nectar availability year-round.
-
Group similar plants together to create dense patches of color that attract hummingbirds from afar.
-
Incorporate vertical elements like trellises for climbing vines such as coral honeysuckle.
-
Provide water sources like shallow birdbaths or fountains for hummingbirds to clean their feathers.
-
Avoid pesticides, which harm both insects (a food source) and birds directly.
Maintenance Tips
To keep your garden thriving:
-
Regularly deadhead spent blooms to encourage continuous flowering.
-
Mulch around plants to retain soil moisture and suppress weeds.
-
Prune shrubs and vines annually to maintain shape and promote growth.
-
Monitor soil conditions; native plants generally require less fertilizer but may benefit from occasional compost applications.
Conclusion
By planting native species such as Eastern red columbine, cardinal flower, bee balm, jewelweed, and butterfly weed, you can create a vibrant sanctuary for hummingbirds in your Eastern U.S. garden year-round. These plants not only attract these remarkable birds but also support local ecosystems by fostering biodiversity.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, incorporating native plants into your landscape is an enriching way to connect with nature while enjoying the beauty of these tiny avian visitors year after year!
If you’ve learned something new about caring for hummingbirds, share the love! Use the buttons on the left to spread this article far and wide. By sharing, you’re helping more people support these fascinating creatures and their well-being. Let’s brighten the world, one hummingbird at a time! Thank you!
Hummingbird Resources That Help You Enjoy Hummingbirds
Here’s a complete guide to attracting hummingbirds to your yard. It lists plants, vines and shrubs that are in bloom for spring, summer and fall. Your hummingbirds will always have flowers to feed on.
Here’s a great article that tells everything you need to know abouthow to choose the best place to hang your hummingbird feeder.
Here’s the best designed hummingbird feederto use. It’s leak proof, so it won’t attract insects and it’s easy to take apart and clean.
Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you clean your hummingbird feeder for those times when the nectar is not changed soon enough and mold starts to grow.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service – Hummingbird Conservation
This site offers detailed information about various hummingbird species, their habitats, and conservation efforts. It also provides resources on how to protect these fascinating birds.
National Park Service – Hummingbird Resources
The National Park Service offers insights into hummingbird species found in national parks, their behaviors, and their role in ecosystems, along with tips for observing them.
Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History – Birds: Hummingbirds
This resource provides educational materials on the role of hummingbirds in pollination and biodiversity, backed by scientific research and exhibits from the Smithsonian.
U.S. Geological Survey – Hummingbird Studies
The USGS offers research on hummingbird migration patterns, population dynamics, and environmental threats, including studies on climate change impacts.